海南医科大学于法标教授团队在Chin Chem Lett期刊上发表学术论文,题目为:A near-infrared two-photon fluorescent probe for the detection of HClO in inflammatory and tumor-bearing mice,DOI: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110531.
A near-infrared two-photon fluorescent probe for the detection of HClO in inflammatory and tumor-bearing mice
Author links open overlay panel,
,
,
,
,
,
- a
- Key Laboratory of Emergency and Trauma, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Haikou Trauma, Key Laboratory of Hainan Trauma and Disaster Rescue, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, China
- b
- Department of Joint Surgery, HongHui Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710054, China
- c
- Department of Comprehensive plastic surgery, Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100144, China
- d
- Engineering Research Center for Hainan Bio-Smart Materials and Bio-Medical Devices, Key Laboratory of Hainan Functional Materials and Molecular Imaging, College of Emergency and Trauma, College of Pharmacy, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571199, China
Received 26 August 2024, Revised 30 September 2024, Accepted 8 October 2024, Available online 10 October 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110531
Abstract
Hypochlorous acid (HClO) is a critical biomolecule in living organisms, playing an essential role in numerous physiological or pathological processes. Abnormal levels of HClO in the body may lead to a series of diseases, for instance, inflammation and cancer. Thus, accurate measurement of HClO levels should be more beneficial for understanding its role in diseases and gaining a deeper insight into the pathogenesis of diseases. In this work, we designed a near-infrared two-photon fluorescent probe (HDM-Cl-HClO) for detecting fluctuations in HClO levels in inflammatory and tumor-bearing mice. Notably, the probe can respond to HClO within 5 s and trigger a brilliant red fluorescence at 660 nm. It exhibits high specificity and sensitivity for HClO. The superior spectral capability of the probe has enabled the detection of HClO levels in cells and zebrafish, as well as achieved the detection of HClO in inflammatory and tumor mice. This work not only provides a novel strategy and tool for HClO imaging in living systems, but also holds great potential for the diagnosis of inflammation and cancer.
Graphical abstract
We have developed a near-infrared two-photon fluorescent probe for the rapid detection of HClO. The probe successfully achieved the tracking of HClO in cells, zebrafish, and mouse model groups of inflammation and tumor, which is expected to be a reliable tool for detecting HClO levels in various disease models.
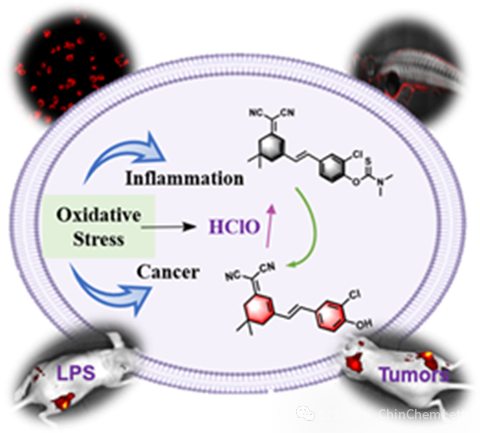
为了研究HClO信号分子在氧化应激中的生理及病理作用,本研究开发了一种双光子近红外荧光探针HDM-Cl-HClO。该探针被成功地应用于LPS诱导的炎症及肿瘤小鼠模型中内源性 HClO水平波动,有助于深入地了解HClO在相关疾病中发挥的作用。
细胞内氧化还原稳态在生理及病理过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。正常情况下,ROS在细胞信号传导和免疫防御中发挥着关键作用。然而,当 ROS 生成过多会引发氧化应激,导致细胞损伤,从而引发多种疾病,如炎症,癌症,糖尿病和神经退行性疾病。HClO作为一种非常重要的 ROS,研究它在生物体内水平的波动可以更好地了解其在生理和病理过程中发挥的作用。目前已开发出许多用于检测HClO 的灵敏且具有选择性的荧光探针。然而,由于穿透深度及自发荧光的限制,生物深层组织成像仍是一个挑战。近红外荧光探针减少了光散射和背景信号的影响,更适合生物荧光成像,同时,双光子探针可以有效提高组织的穿透能力(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310408;Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2404709)。因此,开发近红外双光子荧光探针是解决这一问题的有效策略。
在这项工作中,作者开发了一种近红外双光子荧光探针 HDM-Cl-HClO,用于快速检测炎症和肿瘤环境中的 HClO。在5 s内,探针即可对HClO做出响应,并触发660 nm处荧光信号增强,并对HClO表现出高的灵敏度和特异性。该双光子探针的激发/发射波长都在近红外区域,有效增加了探针在生物系统中的成像深度。HDM-Cl-HClO不仅适用于细胞和斑马鱼模型中HClO 水平波动的检测,其也可以用于炎症和肿瘤小鼠模型中HClO 水平的的检测。该探针的发展为深入研究 HClO 在生物体内的作用机制提供了有力工具,有助于更深入地了解 HClO 在炎症、肿瘤和其他疾病发生发展过程中的作用,从而为疾病的预防、诊断和治疗提供科学依据。

