Fenton-driven photothermal enhanced degradation of methylene blue by using Cu2O@SnO2@PDA cubic heterostructured catalyst
Jingpi Gao a b 1, Shaowen Cheng a b 1, Ping Zhou a b, Jianbo Zhang a, Heying Li a, Yi Zhang a, Manping Lin b, Shuo Gu b, Jinghua Li a b
aCollege of Medical Technology and Engineering, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, China
bThe 1st Affiliated Hospital, Department of Wound Repair, College of Emergency and Trauma, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570100, China
Materials Letters 334 (2023) 133724
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.133724
A B S T R A C T
In order to enhance the photostability of Cuprous oxide and improve the photocatalytic activity, this study was the first to prepare polydopamine (PDA) coated Cu2O@SnO2 Fenton heterostructured catalyst (HCs) for photothermal synergistic enhanced pollutant dye degradation. HCs reduced the Cu2O electron-hole pair filling group rate by Cu/Sn heterostructures, and the PDA shell layer protection greatly improved the stability of Cu2O. The developed Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs could generate heat rapidly under near infrared (NIR) laser irradiation, which greatly improved the catalytic efficiency of the catalyst by a typical photothermal enhanced Fenton-driven degradation process. All the results indicate that Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs have great potential applications in
dye wastewater treatment.
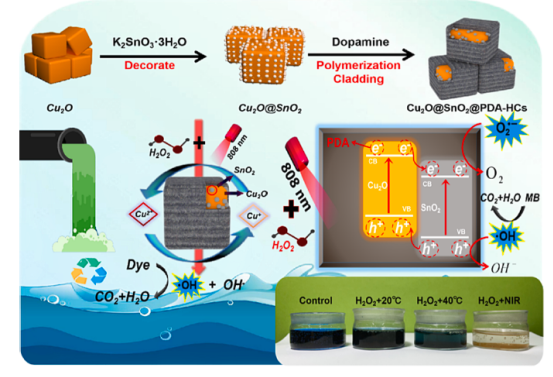
Scheme 1. Schematic degradation mechanism of Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs nanocomposites.
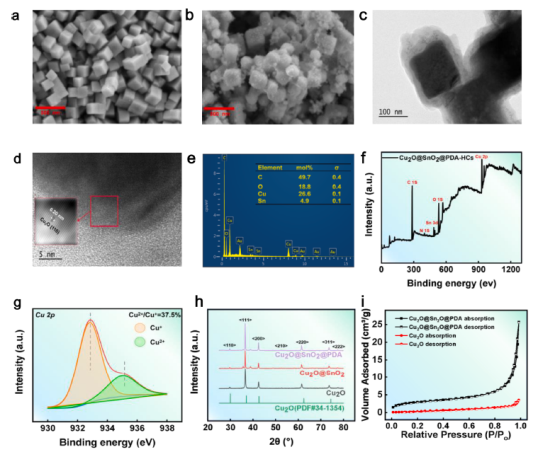
Fig. 1. SEM image of (a) Cu2O nanocatalysts, (b) Cu2O@SnO2 heterostructures, (c) TEM image of Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs, (d) HRTEM image and (e) EDX mapping images. (f) XPS spectrum for Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs and (g) Cu 2p3/2 peak. (h) XRD analysis, (i) N2 adsorption–desorption.
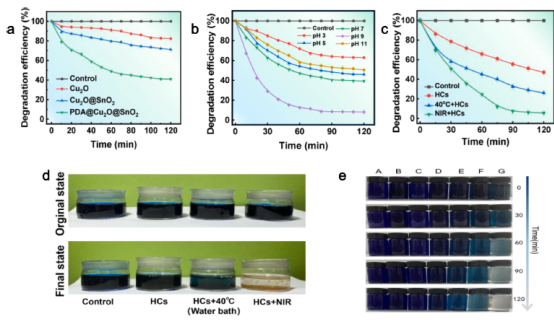
Fig. 2. (a) Catalytic efficiency of Cu2O, Cu2O@Sn2O, Cu2O@Sn2O@PDA-HCs. (b) Degradation efficiency under different pH. (c) Cu2O@Sn2O@PDA-HCs degradation efficiency for MB, (d) Optical photograph of the degradation process. (e) Optical photograph of MB decolorization at different time period. (A: Control, B:H2O2, C: HCs, D-G: HCs + 20, 30,40, 50 ◦C).
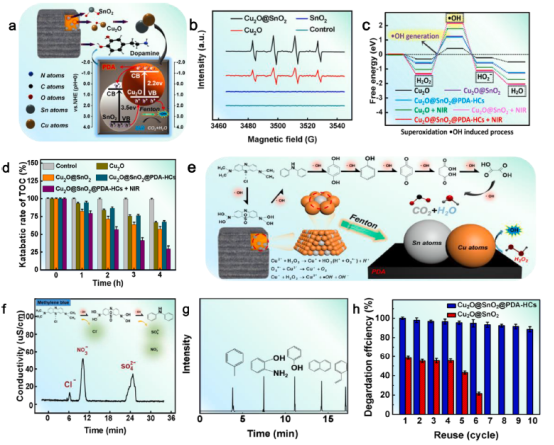
Fig. 3. Degradation mechanism of Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs. (a) Schematic diagram, (b) EPR spectra, (c) DFT calculations of •OH generation, (d) TOC results, (e) Schematic mechanism, (f) Determination of inorganic ions, (g) GC-mass spectra, (h) Reusability.
Conclusion
In summary, NIR-driven photothermal Fenton-like catalysts bimetallic Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs nanocomposites were successfully prepared. Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs improves the photostability and catalytic activity of copper oxide cube, and shows a good degradation effect on dyes. In addition, the nanocomposites can be reused. The results suggest that the photothermal Cu2O@SnO2@PDA-HCs-based Fenton-driven nanocomposites have the potential to perform dye wastewater treatment.

