
Tracking extracellular vesicle phenotypic changes enables treatment monitoring in melanoma
跟踪细胞外囊泡的表型变化实现对黑色素瘤的治疗监测
主讲人:陈星雅
Science Advances丨PubDate:2020-02-26丨DOI:10.1126/sciadv.aax3223
Abstract:
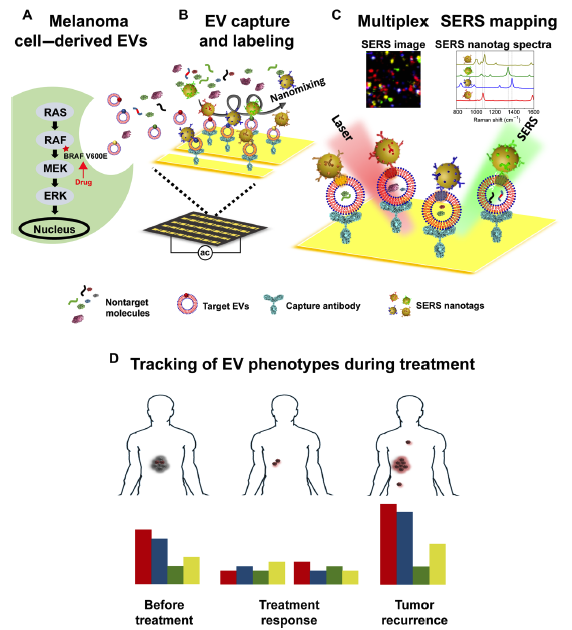
Monitoring targeted therapy in real time for cancer patients could provide vital information about the development of drug resistance and improve therapeutic outcomes. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have recently emerged as a promising cancer biomarker, and EV phenotyping shows high potential for monitoring treatment responses. Here, we demonstrate the feasibility of monitoring patient treatment responses based on the plasma EV phenotypic evolution using a multiplex EV phenotype analyzer chip (EPAC). EPAC incorporates the nanomixing-enhanced microchip and the multiplex surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanotag system for direct EV phenotyping without EV enrichment. In a preclinical model, we observe the EV phenotypic heterogeneity and different phenotypic responses to the treatment. Furthermore, we successfully detect cancer-specific EV phenotypes from melanoma patient plasma. We longitudinally monitor the EV phenotypic evolution of eight melanoma patients receiving targeted therapy and find specific EV profiles involved in the development of drug resistance, reflecting the potential of EV phenotyping for monitoring treatment responses.
摘要:
实时监测针对癌症患者的靶向治疗可以提供有关耐药性发展和改善治疗结果的重要信息。细胞外囊泡(EVs)最近已成为有前途的癌症生物标志物,并且EV表型也具有监测治疗效果的巨大潜力。本文中证明了用一个多重EV表型分析芯片(EPAC)基于血浆EV表型的分析,来监测患者治疗反应的可行性。该芯片结合了纳米混合增强微芯片和多重表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)纳米标签系统,可用于直接EV表型化而无需EV浓缩。在临床前模型中观察到了EV表型异质性和对治疗的不同表型反应。此外,成功地从黑素瘤患者血浆中检测出了癌症特异性的EV表型。通过持续监测八名接受靶向治疗的黑色素瘤患者的EV表型演变,发现了与耐药性发展有关的特定EV信息,证明了利用EV表型分析来监测治疗反应的潜力。

