
Smartphone-triggered targeted inactivation of MRSA under SERS monitoring
SERS 监测下智能手机触发 MRSA 定向灭活
主讲人:周礼
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S174801322300261X
Nano Today. 2023, 53, 102012
Abstract:
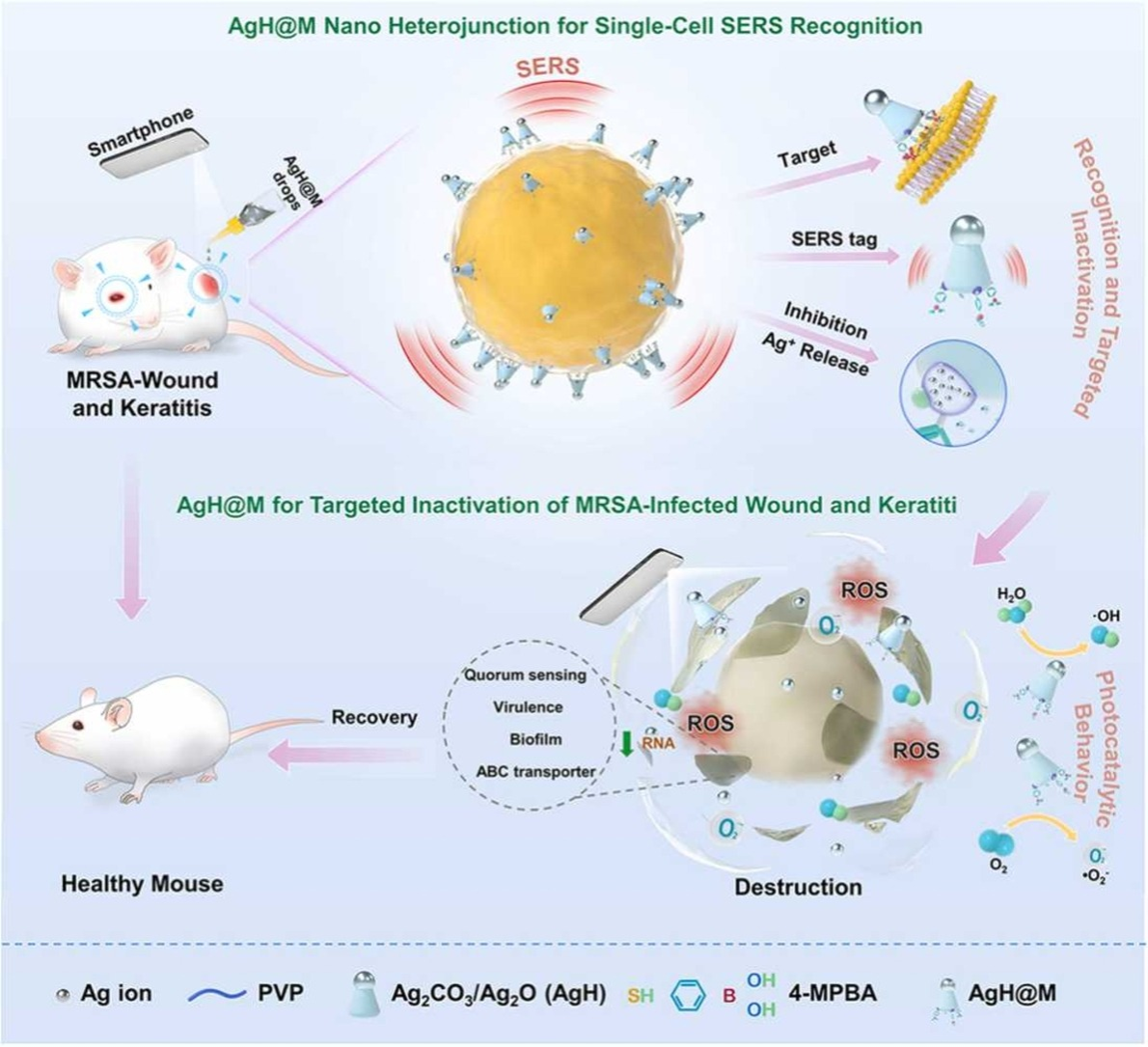
Silver nanoparticles-based multifunctional agents show tremendous potential for simultaneous imaging and against the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-induced superficial infection. However, it is still a challenge to achieve a balance between high precision, high antibacterial efficiency, and biocompatibility. Herein, we present a 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid (4-MPBA)-modified Ag2CO3/Ag2O nano-heterojunctions (AgH@M) that can recognize single MRSA cell by surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and effectively eradicate MRSA under smartphone irradiation. Moreover, the 4-MPBA molecule acts as triple identities for MRSA targeted binding, SERS tag, and inhibition of excessive release of toxic silver ions for the Raman Imaging guided bacterial treatment. AgH@M simultaneously targeted binding on the surface of bacteria and made full use of the released limited Ag+ into the MRSA, thereby reducing the toxicity to mammalian cells. In addition, the potential antibacterial mechanism involves ROS production from photocatalytic behavior, interference with functional genes of quorum sensing, virulence, biofilm, and ATP-binding cassette transporter. Also, the AgH@M can monitor the residual bacteria in MRSA-infected wounds and keratitis animal models in real-time for at least 7 days by SERS and accomplishes a satisfactory therapeutic effect. This work may provide promising visualized heterojunctions for the targeted eradication of MRSA with a portable light source.
摘要:
基于银纳米颗粒的多功能制剂在同时成像和对抗耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA)引起的浅表感染方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,如何实现高精度、高抗菌效率和生物相容性之间的平衡仍然是一个挑战。在此,我们提出了一种4-巯基苯硼酸(4-MPBA)修饰的Ag 2 CO 3 /Ag 2 O纳米异质结(AgH@M),可以通过表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)识别单个MRSA细胞并有效根除智能手机照射下的 MRSA。此外,4-MPBA 分子作为 MRSA 靶向结合、SERS 标签和抑制有毒银离子过度释放的三重身份,用于拉曼成像引导细菌治疗。AgH@M同时靶向结合在细菌表面,充分利用释放的有限Ag +进入MRSA,从而降低对哺乳动物细胞的毒性。此外,潜在的抗菌机制涉及光催化行为产生ROS、干扰群体感应、毒力、生物膜和ATP结合盒转运蛋白的功能基因。此外,AgH@M可以通过SERS实时监测MRSA感染伤口和角膜炎动物模型中的残留细菌至少7天,并取得令人满意的治疗效果。这项工作可能为利用便携式光源有针对性地根除 MRSA 提供有前景的可视化异质结。

