
关键词:
β-半乳糖苷酶;近红外;荧光探针;溶酶体;细胞衰老
原文链接:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/smo.20240062
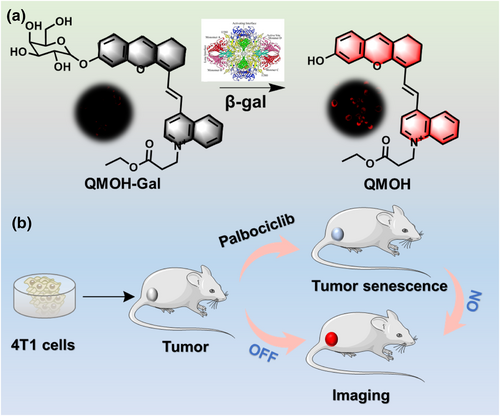
细胞衰老可能导致邻近健康细胞衰老,进而引起炎症、神经系统疾病和动脉粥样硬化等多种疾病的发生。本文发展了一种β-半乳糖苷酶近红外荧光探针,成功用于正常细胞与衰老细胞的区分,实现了对斑马鱼体内β-半乳糖苷酶的监测,并对帕博昔布诱导的乳腺肿瘤衰老过程中β-半乳糖苷酶的跟踪,有助于更深入地了解细胞衰老在生理过程和疾病发生发展过程的作用。
随着年龄的增长,体内细胞、组织和器官的功能降低,这可能导致机体免疫系统受损,进而导致衰老细胞的积累。而衰老细胞的积累可进一步损害组织功能。衰老细胞在一系列生理和病理过程中发挥着关键作用,例如癌症、伤口愈合和重塑以及其它与年龄相关的疾病。此外,衰老被认为是许多慢性病、神经系统疾病和人类健康下降的重要因素。因此,细胞衰老的早期诊断和有效清除迫在眉睫。监测疾病相关的生物标志物可以有效地获得诊断和预后信息,以及了解它们在疾病发展中的重要作用。β-半乳糖苷酶是人体内一种重要的糖苷水解酶,其可以催化多种糖蛋白和乳糖的水解。β-半乳糖苷酶在多种生理过程中发挥重要作用,与细胞衰老密切相关,已被认为是细胞衰老的主要生物学标志物之一。因此,监测β-半乳糖活性对于细胞衰老以及老年相关疾病的早期诊断具有重要意义。
近日,海南医科大学于法标教授团队开发了一种用于检测β-半乳糖苷酶的溶酶体靶向且酸性条件稳定的近红外荧光探针(QMOH-Gal)。在β-半乳糖苷酶存在下,该探针QMOH-Gal在近红外区域发射出强的荧光信号。此外,QMOH-Gal对β-半乳糖苷酶展现出高的选择性和敏感性。该探针不仅能有效地定位于溶酶体中,而且已成功应用于正常细胞和衰老细胞的区分。QMOH-Gal也成功应用于斑马鱼β-半乳糖苷酶的检测。重要的是,该探针可以在药物诱导的衰老小鼠肿瘤模型中追踪衰老细胞。
如图1所示,通过对探针的紫外和荧光光谱分析,探针对β-半乳糖苷酶展现出优异的光谱特性,例如低的检测限,高的特异性,强的光稳定性以及快速的响应。此外,在酸性条件下,该探针与β-半乳糖苷酶反应后荧光信号保持稳定,这为在溶酶体中检测β-半乳糖苷酶提供了坚实的基础。我们进一步研究了该探针能否定位于活细胞的溶酶体中。通过一种市售溶酶体染料与我们的探针共同孵育用于研究,结果表明探针QMOH-Gal能有效地在细胞溶酶体中聚集。
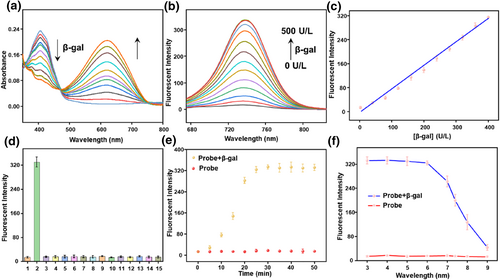
FIGURE 1 Spectral properties of the probe QMOH-Gal (10 μM) to β-gal in PBS containing 5% DMSO (pH = 7.4, 10 mM). (a) The ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum and (b) the fluorescence spectrum of QMOH-Gal (10 μM) for β-gal (0–500 U/L, λex = 640 nm, slit widths: 5/5 nm). (c) The linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity of QMOH-Gal and β-gal (0–400 U/L). (d) The reaction of QMOH-Gal to a series of various analytes: (1) blank, (2) β-gal (500 U/L), (3) esterase (500 U/L), (4) ALP (500 U/L), (5) AFU (100 U/L), (6) Cys (1 mM), (7) Hcy (1 mM), (8) GSH (1 mM), (9) BSA (100 μg/ml), 10. HClO (100 μM), (11) NaNO2 (100 μM), (12) H2O2 (100 μM), (13) Cl− (100 μM), (14) Na+ (100 μM), (15) K+ (100 μM). Fluorescence spectrum at 740 nm of QMOH-Gal (e) with time change and (f) pH effect to β-gal at 37°C.
随后,我们研究了该探针QMOH-Gal在细胞内监测β-半乳糖苷酶的能力。我们选用不同的细胞系,并用不同的方式诱导细胞衰老。对LO2细胞,用阿霉素处理5天可诱导细胞衰老,对于HepG2细胞,我们选择XL413处理,对于4T1细胞,我们选择帕博昔布。随后,我们X-gal染色验证了衰老模型是否成功建立(图2A)。与未处理细胞相比,药物处理细胞呈现明显的蓝色,说明细胞衰老模型的建立是成功的。接下来,我们研究了探针用于准确诊断细胞衰老的能力。如图2所示,在衰老细胞中获得了明亮的红色荧光信号,这不仅表明探针QMOH-Gal可以用于检测β-半乳糖苷酶,而且还表明β-半乳糖苷酶在衰老细胞中的水平相对较高。结果表明,该探针QMOH-Gal可用于细胞内β-半乳糖苷酶的检测,并能有效区分衰老细胞与其他细胞系,有助于衰老相关疾病的诊断。
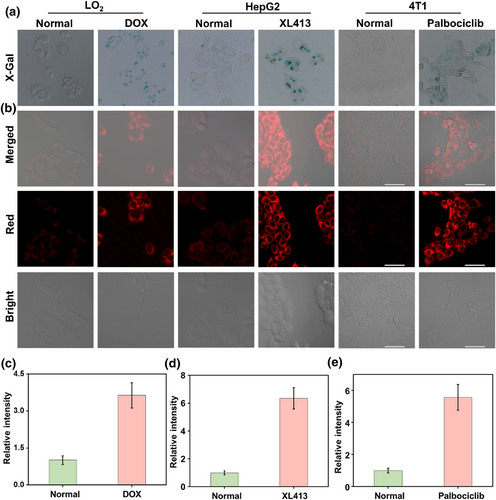
FIGURE 2 Visualization imaging of intracellular β-gal. (a) X-Gal staining of endogenous β-gal in LO2 cells and DOX-induced LO2 senescent cells, HepG2 cells and XL413-induced HepG2 senescent cells, and 4T1 cells and palbociclib-induced 4T1 senescent cells. (b) Fluorescence imaging of β-gal with QMOH-Gal in LO2 cells and DOX-induced LO2 senescent cells, HepG2 cells and XL413-induced HepG2 senescent cells, and 4T1 cells and palbociclib-induced 4T1 senescent cells. (c) Relative fluorescent intensities in LO2 cells and DOX-induced LO2 senescent cells. (d) Relative fluorescent intensities in HepG2 cells and XL413-induced HepG2 senescent cells. (e) Relative fluorescent intensities in 4T1 cells and palbociclib-induced 4T1 senescent cells. λex = 640 nm, λem = 680–770 nm. Scale bars: 50 μm.
接下来,我们研究了探针在体内可视化β-半乳糖苷酶的能力。如图3所示,我们首先建立了4T1肿瘤小鼠模型,并将其分为两组。一组不接受任何治疗(肿瘤组),另一组给予帕博昔布诱导肿瘤衰老(肿瘤衰老组),然后进行体内成像。通过H&E和Ki67染色,我们验证了肿瘤以及肿瘤衰老模型的成功建立。随后,我们对小鼠进行了活体成像。与肿瘤组相比,帕博昔布诱导的肿瘤衰老组显示出更强的荧光信号,表明该探针能够有效地可视化体内肿瘤衰老。上述研究结果证实,该探针可有效用于衰老过程中β-半乳糖苷酶的精确跟踪,并可作为检测衰老相关疾病的有效工具。
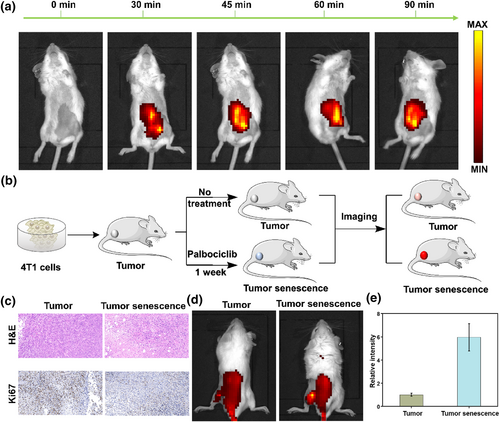
FIGURE 3 Imaging endogenous β-gal in mice. (a) Imaging β-gal in the mouse peritoneal cavity at different time points (0–90 min). (b) Schematic diagram of mouse tumor and senescence tumor modeling. (c) H&E and Ki67 staining for mouse tumors and palbociclib-induced tumor senescence. (d) Imaging of β-gal in mice tumor and senescence tumor modeling. (e) Relative fluorescence intensity in (d). λex = 640 nm, λem = 680–770 nm.
CONCLUSION
In summary, we developed a novel lysosome NIR fluorescent probe (QMOH-Gal) for sensitive and rapid monitoring of β-gal, which exhibits excellent properties such as good biocompatibility, high selectivity and sensitivity, as well as a wide linear range. This probe can not only be used to distinguish senescent cells from other non-senescent cells but also for visual tracking of β-gal detection in zebrafish models. Importantly, the probe has also been successfully applied for the precise tracking of β-gal in aging tumors, contributing to the diagnosis of age-related diseases. We believe that the designed probe may serve as an effective tool for studying age-related diseases.
以上研究论文以“A β-galactosidase Activated Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe for Tracking Cellular Senescence In Vitro and In Vivo”为题发表于 Smart Molecules 期刊,论文第一作者为海南医科大学临床专业博士生苏天,通讯作者为海南医科大学于法标教授和罗贤柱助理研究员。

