Nano Today | In Situ Phagocyte-mediated Deep Tumor Penetration Assisted by ApoA-1 Mimetic Peptide-modified Silicasome
原位吞噬细胞介导多肽-硅脂质体的肿瘤深度渗透和ICG光热效应增强
主讲人:王俊杰
DOI: 10.1016/j.nantod.2023.101864
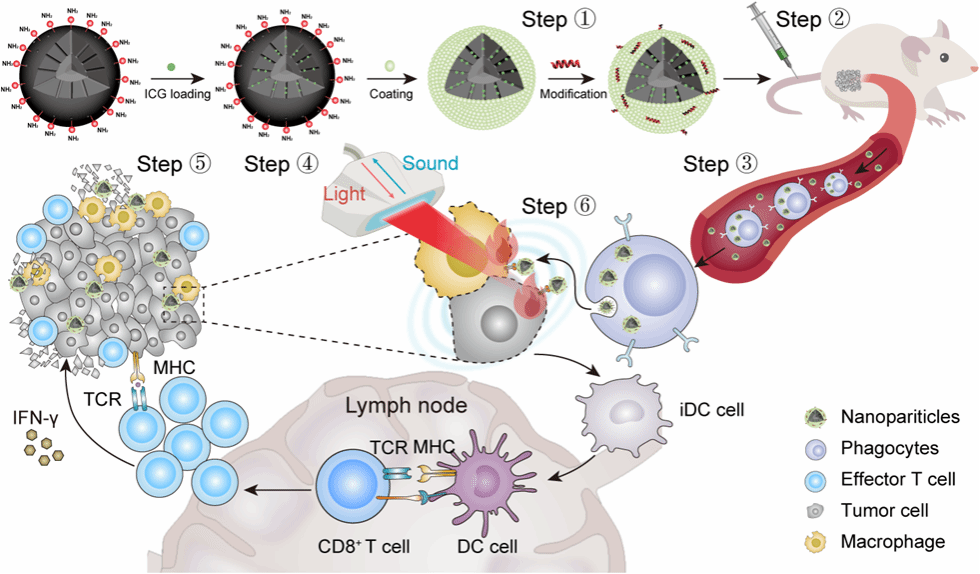
Deep tumor penetration of therapeutic drugs remains challenging for the ablation of solid tumors, which impedes their clinical translation. In situ cell-mediated delivery is an efficient strategy for deep drug tumor penetration. Herein, we designed a visible mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN) with indocyanine green (ICG) loading, lipid encapsulation and ApoA-1 mimetic peptide (R4F) modification, denoted R4F-ICG@L-MSN. The peripheral blood experiment and immunofluorescence reveal that with the aid of scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1) targeting ability, R4F ICG@L-MSNs could be specially transported by the in situ phagocyte-mediated delivery and efficiently taken up by 4T1 tumor cells and macrophages, achieving deep penetration and wide distribution in solid tumors. The visualized phototheranostic (photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy) verified that the deep tumor penetration of R4FICG@L-MSNs enhance the efficiency of treatment for solid tumors, accompanied by the reversed immunosuppressive microenvironment. Such multifunctional R4FICG@L-MSNs achieved tumor targeting, deep penetration, photoacoustic imagingguided photothermal therapy and enhanced anti-tumor immune response, indicating advancements toward deep penetration in tumors and promoting effects for multimodality therapies.
恶性肿瘤严重危害人类的健康与生命。由于实体瘤表现出显著的异质性、缺氧、供血不足和间质流体压力增加,大多数纳米药物无法充分穿透肿瘤,导致诊断和治疗效果不佳。药物的深度渗透仍然是癌症治疗的一个挑战性问题。一般来说,纳米药物的深度渗透策略分为两类:一类是以尺寸为特征而精心设计的纳米平台,包括CAPIR五步级联递送(血液循环、肿瘤积累、深层渗透、细胞内化和药物释放)与尺寸收缩递送;另一类是细胞介导的药物递送(又称为特洛伊木马策略)。前者通过血管外渗、肿瘤内渗透压的增加、EPR效应等实现肿瘤的深度渗透。后者通过活细胞或人工分离的细胞膜负载纳米颗粒向肿瘤区域的特异性递送,是利用细胞的生理功能,达到优化成像和治疗的效果。但其制备过程仍较为复杂,且肿瘤渗透效果易受肿瘤异质性的影响。因此,开发操作简单且具有深度肿瘤渗透性的纳米药物,将有助于临床转化。
研究团队开发了一种可视化的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒(MSN),其负载吲哚菁绿(ICG)、外部由脂质包封、表面由apoA-1模拟肽(R4F)修饰,命名为R4F�ICG@L-MSN。研究结果表明,R4F-ICG@L-MSN具有肿瘤内深度渗透与有效驻留、ICG的高效装载与光热效应提升、以及光热效应诱导的抗肿瘤免疫应答等性能,致使其光声成像能力和光热效应显著提升,由此展现了良好的光声成像引导的肿瘤光热治疗效果。

